As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and managing our health becomes increasingly important. One common health concern that affects many older adults is hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by low blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia in elderly individuals can have significant implications for their overall well-being and requires careful attention and management. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective strategies to deal with hypoglycemia in the elderly, ensuring their safety and quality of life.
What is Hypoglycemia in Elderly?
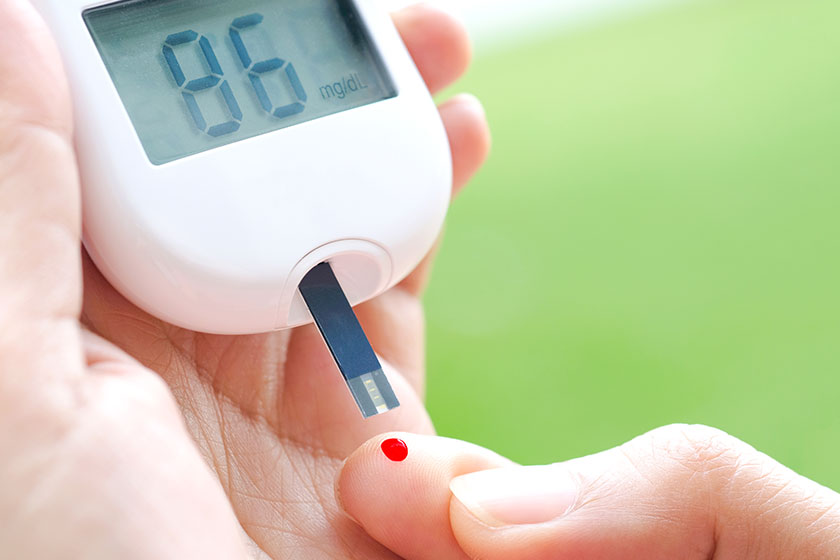
Hypoglycemia occurs when the blood glucose levels drop below the normal range, usually defined as less than 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). In older adults, the condition may arise due to various factors, including certain medications, changes in eating patterns, underlying health conditions, or poorly controlled diabetes. It is particularly common in older adults with diabetes who take insulin or other blood sugar-lowering medications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Identifying the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in the elderly is crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. Some common symptoms include:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Sweating or clammy skin
- Shakiness or trembling
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blurred vision
- Headaches or migraines
- Anxiety or irritability
- Hunger or sudden cravings
- Rapid heartbeat
It is important to note that symptoms may vary among individuals, and some elderly individuals may not experience noticeable signs of hypoglycemia. Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to catch and address low blood sugar levels promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hypoglycemia in the elderly can stem from a combination of factors, including:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as insulin or oral diabetes drugs, can lower blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Changes in Eating Habits: Irregular meal patterns, skipping meals, or inadequate food intake can disrupt the balance of blood sugar levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol without eating sufficient food can lead to hypoglycemia in elderly individuals.
- Kidney or Liver Dysfunction: Impaired kidney or liver function can affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Changes: Aging can result in hormonal imbalances, affecting insulin production and utilization in the body.
Managing Hypoglycemia in Elderly
Effective management of hypoglycemia in the elderly involves a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle adjustments, medication management, and supportive care. Here are some essential strategies:
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Theelderly should monitor their blood glucose levels regularly, especially if they have diabetes or are taking medications that can lower blood sugar.
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a well-balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods, opting for complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy.
- Medication Review: Work closely with healthcare professionals to review and adjust medications as needed to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Meal Planning: Establish regular meal patterns and avoid skipping meals. Small, frequent meals and snacks throughout the day can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Alcohol Awareness: Advise the elderly to consume alcohol in moderation and always with food to prevent a sudden drop in blood sugar levels.
- Emergency Preparedness: Ensure elderly individuals have a plan in place for managing hypoglycemia emergencies. This includes carrying glucose tablets or gel, wearing medical alert bracelets, and informing family members, friends, or caregivers about the condition.
- Regular Exercise: Encourage the elderly to engage in physical activity appropriate for their fitness level. Regular exercise can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Ongoing Medical Care: Regular visits to healthcare professionals are crucial for monitoring blood sugar levels, adjusting medications, and addressing any underlying health issues.
Time to Contain Hypoglycemia in Elderly
Hypoglycemia in the elderly requires careful attention and management to ensure their safety and well-being. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective strategies, elderly individuals and their caregivers can effectively navigate this condition. Regular monitoring, a balanced diet, medication management, and lifestyle adjustments form the pillars of hypoglycemia management in the elderly. With proper care and support, elderly individuals can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their blood sugar levels.